已知函数 \(g\left ( {x} \right )=λx+\mathrm{sin}x\) 是区间 \([ - 1\),\(1]\) 上的减函数.
(Ⅰ)若 \(g(x)⩽{t^2} + \lambda t + 1\) 在\(x \in [ - 1\),\(1]\)及\(\lambda \)所在的取值范围上恒成立,求\(t\)的取值范围;
(Ⅱ)试讨论函数\( \mathrm{h}\left(x\right)=\frac{\mathrm{ln}x}{f\left(x\right)}-{x}^{2}+2ex-m\)的零点的个数.
(Ⅰ)由 \( g\text{'}\left(x\right)=\lambda +\mathrm{cos}x\)
又 \(\because g(x)\) 在 \([ - 1\),\(1]\) 上单调递减, \(\therefore g'(x)⩽0\) 在 \([ - 1\),\(1]\) 上恒成立.
\(\therefore \lambda ⩽ - \cos x\) 对 \(x \in [ - 1\),\(1]\) 恒成立,\( \because {[-\mathrm{cos}x]}_{min}=-1\) \(\therefore \lambda ⩽-1\)
\(\because g(x)⩽{t^2} + \lambda t + 1\) 在 \(x \in [ - 1\),\(1]\) 上恒成立,即 \(g{(x{)}_{\text{max}}}⩽{{t}^{2}}+\lambda t+1\)
\(\because g{(x)_{max}} = g( - 1) = - \lambda - \sin 1\) , \(\therefore - \lambda - \sin 1⩽{t^2} + \lambda t + 1\) ,即 \((t + 1)\lambda + {t^2} + \sin 1 + 1⩾0\) 对 \(\lambda ⩽ - 1\) 恒成立。
令 \(F(\lambda ) = (t + 1)\lambda + {t^2} + \sin 1 + 1(\lambda ⩽ - 1)\) ,则 \(\left \{ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {t+1⩽0} \\\ {-t-1+{{t}^{2}}+\sin {1}+1⩾0} \end{array} \right .\)
\(\therefore \) \(\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {t⩽ - 1} \\\ {{t^2} - t + \sin 1⩾0} \end{array}} \right.\) , \(\therefore t⩽ - 1\)
(Ⅱ)讨论函数\( \mathrm{h}\left(x\right)=\frac{\mathrm{ln}x}{x}-{x}^{2}+2ex-m\)的零点的个数,即讨论方程 \( \frac{\mathrm{ln}x}{x}={x}^{2}-2ex+m\) 根的个数.令\( {f}_{1}\left(x\right)=\frac{\mathrm{ln}x}{x}\), \( {f}_{2}\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-2ex+m\),
\( \because {f}_{1}^{\text{'}}\left(x\right)=\frac{1-\mathrm{ln}x}{{x}^{2}}\),\(\therefore \)当\( \mathrm{x}\in \left(0,e\right)\)时, \({f_1}\prime (x) > 0\) ,\(\therefore {f_1}(x)\) 在\( \left(0,e\right)\)上为增函数;
当\( \mathrm{x}\in \left(e,+\mathrm{\infty }\right)\)时, \({f_1}\prime (x) < 0\) , \(\therefore {f_1}(x)\) 在\( \left(e,+\mathrm{\infty }\right)\)上为减函数,
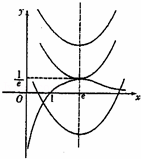
\(\therefore \)当\( \mathrm{x}=\mathrm{e}\)时,\( {f}_{1}{\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}_{max}={f}_{1}\left(e\right)=\frac{1}{e}\) 而\( {f}_{2}\left(x\right)={\left(x-e\right)}^{2}+m-{e}^{2}\),
\(\therefore \)函数 \({f_1}(x)\) 、 \({f_2}(x)\) 在同一坐标系的大致图象如图所示,
\(\therefore \)①当\( \mathrm{m}-{e}^{2}>\frac{1}{e}\),即\( \mathrm{m}>{e}^{2}+\frac{1}{e}\)时,方程无解.函数 \(h(x)\) 没有零点;
②当\( \mathrm{m}-{e}^{2}=\frac{1}{e}\),即\( \mathrm{m}={e}^{2}+\frac{1}{e}\)时,方程有一个根.函数 \(h(x)\) 有1个零点
③当\( \mathrm{m}-{e}^{2}<\frac{1}{e}\),即\( \mathrm{m}<{e}^{2}+\frac{1}{e}\)时,方程有两个根.函数 \(h(x)\) 有2个零点